What Is circRNA and how to Study It by Sequencing?

Introduction to circRNA Sequencing circRNA is a new type of non-coding RNA (ncRNA) produced by non-sequential exon, intron, or both backsplicing. Their covalently closed loop feature, which implies they lack 5′ end caps and 3′ poly-A tails, differentiates them. Because of their nuclease resistance, circRNAs are highly stable forms of ncRNAs. When circRNAs were unearthed in […]
Biological Function and Sequencing Technologies of m1A RNA Modification

Introduction to N1-methyladenosine (m1A) Sequencing In eukaryotic cells, N1-methyladenosine (m1A) is found in thousands of different gene transcripts (from yeast to mammals). The majority of m1A methylation modifications occur in the 5’UTR region of mRNA, and it is a common post-transcriptional modification in tRNA and rRNA in eukaryotes. m1A at the first and second nucleotides of the […]
The Use of Biotinylated Nucleic Acids
Biotinylated nucleic acids are increasingly recognized as powerful tools in molecular biology and genetic research. The incorporation of biotin into nucleic acid molecules, such as DNA and RNA, allows for enhanced detection, isolation, and manipulation of these biomolecules. This article explores the significance, applications, and methodologies related to the use of biotinylated nucleic acids. What Are […]
What is the RNA Integrity Number (RIN)?
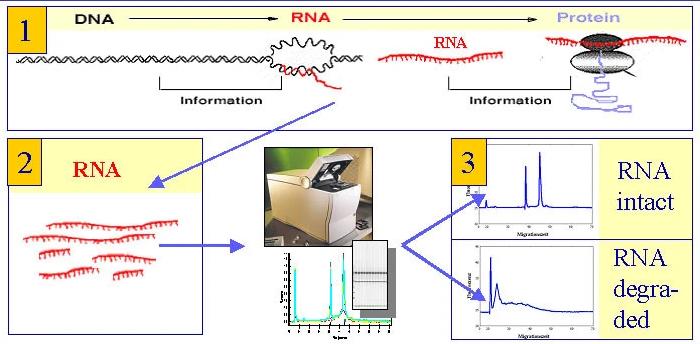
Overview At CD Genomics, we pride ourselves on the quality of the long read long sequencing data we generate for Pacific BioSciences (PacBio) and Oxford Nanopore Technology (ONT). High-quality sequencing data is the ultimate goal of next-generation sequencing. Since the final quality is largely dependent on the quality of the starting material, it is important to ensure high-quality starting material. Unlike […]
High-Molecular-Weight DNA Extraction for Long-Read Sequencing
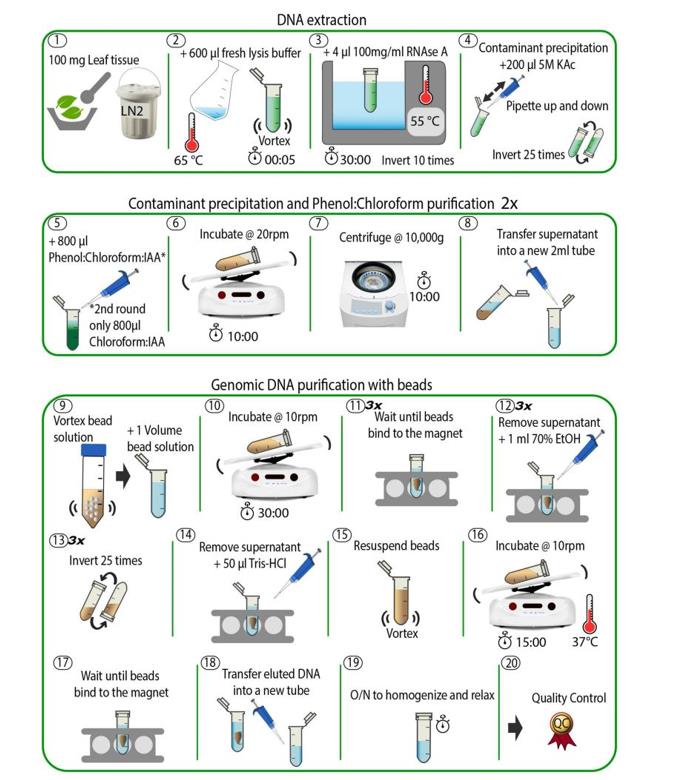
Long-read sequencing technology requires high molecular weight DNA of sufficient purity and integrity because the quality of the DNA starting material will be directly reflected in the sequencing results. Any irreversible DNA damage present in the input material (e.g., interstrand cross-links, etc.) will result in compromised performance and reduced read length. Contamination present in the sample […]